OIE/FAO/WHO/IVPHC
Background Discussion
27 July
2010
Humanitarian Resource Institute
Phone: (203) 668-0282
Url: www.humanitarian.net
Pathobiologics International:
Url: www.pathobiologics.org
HRI:UNArts - Millennium Medicine Project
Url: www.unarts.org/mmp

EID
Surveillance
Notes
MMP: Hospital Acquired Infections - Surveillance,
Containment
& Control
Dear Colleagues:
According to the Clinicians
Biosecurity
Network, Airborne Spread of
Current
U.S. healthcare discussions are focused on insurance companies denying
coverage
for hospital-acquired conditions [1],
rather than taking full responsibility for a lack of biosecurity
measures
and compensation for the victim of resultant
complications. In 2002, an estimated 1.7 million
healthcare-associated
infections occurred in the United States, resulting in 99,000 deaths.
[2] Methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was reported to
have
killed 48000 Americans in one year [3] and Clostridium
Difficile [4,5,6,7] being more common than MRSA in
Southeast Community
Hospitals. [8] Clostridium difficile [9] represents a major problem at
hospitals
across the United States.
The true spectrum of pathogens associated with clinical disease was a
topic at "The Future of Biodetection Systems Workshop" sponsored by Los
Alamos
National Laboratory in 2006. [10] The conference brought together
industry,
academia, national labs, and federal agency personnel in an interactive
process, to develop a roadmap for research and development investment
in biodetection. In my presentation, DNA-based Detection
Technologies
[11] included a focus on full spectrum pathogen detection, [12]
including
tools that could be used for environmental analysis of hospitals.
Today, veterinary medicine is the lead academic reference point for
environmental contamination and agricultural impact of high consequence
pathogens that contribute to the landscape of human disease. Recent
discussions regarding Zoonotic diseases [13,14] include:
-
Methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus in Horses and Horse Personnel. [15,16]
-
Presence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in farm and pet animals.
[17]
-
National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS):
[18]
-
Life-Threatening Infantile Diarrhea from Fluoroquinolone-Resistant
Salmonella enterica
Typhimurium with Mutations in Both gyrA and parC. [19]
- Nosocomial
Outbreak of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Infection. [20]
-
Co-Infection A-Fujian-H3N2 - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus
Aureus: VRE, MRSA, and Influenza. [21]
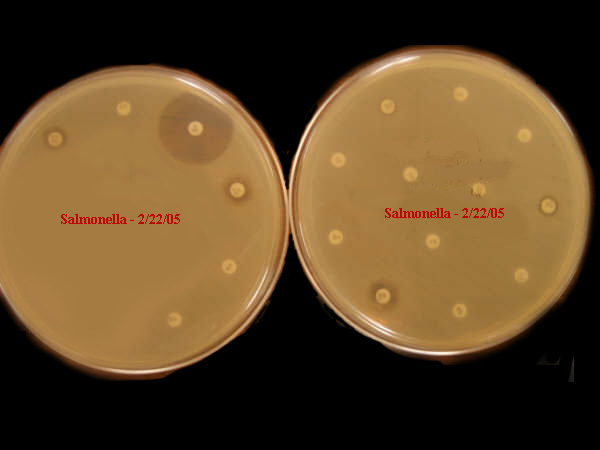
|
Antibiotic Sensitivity:
Salmonella
U.S. Test: Agricultural
Operations February
2005
Embracing challenges
associated with drug resistant pathogens, water conservation
initiatives, environmental contamination, agricultural and public
health impact.
Veterinarians note that human
physicians
have no clue regarding the true scope of pathogens with full antibiotic
resistance
in the clinical disease landscape.
|
Today,
the "One Health
Initiative," is a movement to forge co-equal, all inclusive
collaborations
between physicians, veterinarians, and other scientific-health related
disciplines,
has been endorsed by various major medical organizations and health
agencies,
including the American Veterinary Medical Association, the American
Medical
Association, the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, the
American Society for Microbiology and the Centers for Disease Control
and
Prevention (CDC). Additionally, more than 400 prominent scientists,
physicians
and veterinarians worldwide have endorsed the initiative. --
HRI:UNArts: One Health Initiative Unites Human and Veterinary
Medicine.
[22]
Surveillance, containment and control of high consequence pathogens in
the world's wealthiest countries, highlight the difficult task of
strategic planning and development to optimize public health
infrastructure, for the 5 billion target demographic of the Millennium
Medicine Project.
Corporations, physicians, veterinarians, scientists
that would like
to serve in an advisory or low cost product development role (included
in the Millennium Medicine Project medical equipment and
supplies
portal), are asked to contact:
Stephen M. Apatow
Founder, Director of Research & Development
Humanitarian Resource Institute
Humanitarian University Consortium Graduate Studies
Center for Medicine, Veterinary Medicine & Law
Phone: 203-668-0282
Email: s.m.apatow@humanitarian.net
Internet: www.humanitarian.net
Pathobiologics International
Internet: www.pathobiologics.org
Humanitarian
Intervention Initiative
Operational Security Consultancy
Internet: www.H-II.org
References:
1. HM Takes the Lead on Interventions and Lessens Financial Impact on
Institutions'
Bottom Line: The Hospitalist, Medscape Today, 23 July 2010. Url:
http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/724087
2. Klevens RM, Edwards JR, Richards CL, et al. Estimating
healthcare-associated
infections in US hospitals, 2002. Public Health Rep. Mar
2007;122(2):160-6.
3. Hospital-Acquired Infections, MRSA, Killed 48,000
Americans In One Year: Medical News Today. 23 February 2010. Url:
http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/180065.php
4. Clostridium difficile in broiler chickens sold at market
places in Zimbabwe and their antimicrobial susceptibility:
International Journal of Food Microbiology
Volume 124, Issue 3, 10 June 2008, Pages 268-270. Full text preview:
http://www.springerlink.com/content/125323n1x35176n4/
5. A possible role for Clostridium difficile in the etiology of calf
enteritis: Vet Microbiol. 2008 Mar 18;127(3-4):343-52. Epub 2007
Sep 18. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17964088
6. Molecular characterization of Clostridium difficile isolates
from horses in an intensive care unit and association of disease
severity with strain type:
Journal of the American Veterinary
Medical Association, March 1, 2006, Vol. 228, No. 5, Pages 751-755,
doi: 10.2460/javma.228.5.751
Url:
http://avmajournals.avma.org/doi/abs/10.2460/javma.228.5.751?journalCode=javma
7. Clostridium difficile in Retail Meat Products, USA, 2007: Songer JG,
Trinh HT, Killgore GE, Thompson AD, McDonald LC, Limbago BM.
Clostridium
difficile in retail meat products, USA, 2007. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009
May;
[Epub ahead of print]. Url:
http://www.cdc.gov/eid/content/15/5/pdfs/08-1071.pdf
8. 4. In Southeast Community Hospitals Clostridium Difficile Is More
Common Than MRSA: Medical News Today, 23 March 2010.
http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/183170.php
9. Airborne Spread of
Clostridium
difficile: Clinicians Biosecurity Network, 14 May 2010. Url:
http://www.upmc-cbn.org/report_archive/2010/05May_2010/cbnreport_05142010.html
10. The Future of Biodetection Systems Workshop sponsored by Los Alamos National
Laboratory, 2006. Url: http://www.lanl.gov/bioscience/biodetection.shtml
11. DNA-based Detection Technologies: Stephen M. Apatow, PPT
Presentation
The Future of Biodetection Systems Workshop hosted by the Los Alamos National
Laboratory, 2006. Url:
http://www.pathobiologics.org/btac/lanl/bioscience/ref/SMABDS_Final.pdf
12. Optimization and clinical validation of a pathogen detection
microarray: Genome Biology 2007, 8:R93. Url:
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.139.4456&rep=rep1&type=pdf
13: One Medicine: One Health (Zoonotic Disease) Online
Course: Medicine:
Humanitarian Resource Institute, Pathobiologics International. Url:
http://www.humanitarian.net/biodefense/fazdc/zdc1/
14. Antibiotic Resistance - Enteric Disease: Equestrian Industry,
Pathobiologics International. Url:
http://www.pathobiologics.org/ivphc/ar362005.html
15. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Horses and Horse
Personnel, 2000–2002: CDC Emerging Infectious Disease, Vol. 11, No. 3,
March 2005. Url: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol11no03/04-0481.htm
16. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An emerging problem in
horses?: JAVMA, 15 November 2003. Url:
http://www.avma.org/onlnews/javma/nov03/031115a.asp
17. Presence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in
farm and pet animals: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Oct
1996, 2285-2287, Vol 40, No. 10. Url:
http://aac.asm.org/cgi/content/abstract/40/10/2285
18. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (NARMS): A list
of all publications from peer-reviewed medical literature
using NARMS data. Url: http://www.cdc.gov/NARMS/
19. Life-Threatening Infantile Diarrhea from Fluoroquinolone-Resistant
Salmonella enterica Typhimurium with Mutations in Both gyrA and parC:
CDC Emerging Infectious Diseases, Vol. 9, No. 2, February 2003. Url:
http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol9no2/02-0185.htm
20. Nosocomial Outbreak of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella
Infection, NEJM, Volume 344:1572-1579, Number 21, May 24, 2001.
Url:
http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/abstract/344/21/1572?view=abstractpmid=11372008
21. Co-Infection A-Fujian-H3N2 - Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus
Aureus: VRE, MRSA, and Influenza: Emergence of Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus as a Cause of Community-Acquired Pneumonia During
the Influenza Season, 2003-2004. Url:
http://www.humanitarian.net/biodefense/fazdc/influenza_mrsa12903.html
22. HRI:UNArts: One Health Initiative Unites Human and Veterinary
Medicine: Humanitarian Resource Institute,
23 February 2010. Url: http://www.unarts.org/news/onehealth_2222010.html
|